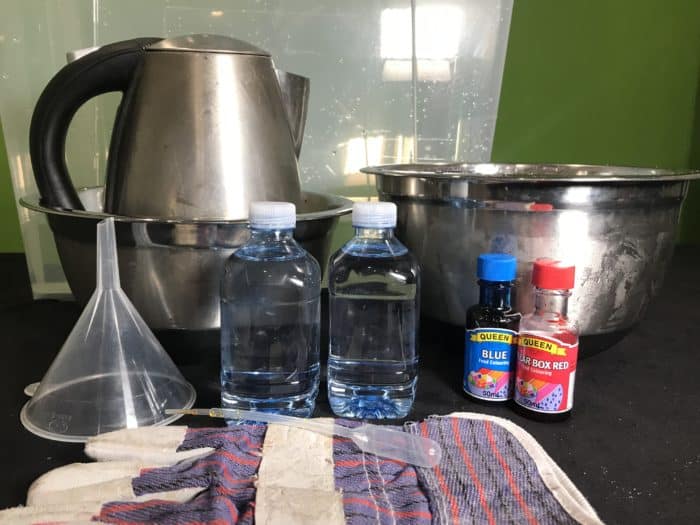
You Will Need:
- One Kettle
- Gloves
- One Funnel
- A large clear container
- One ice bath in a large bowl
- One empty bowl
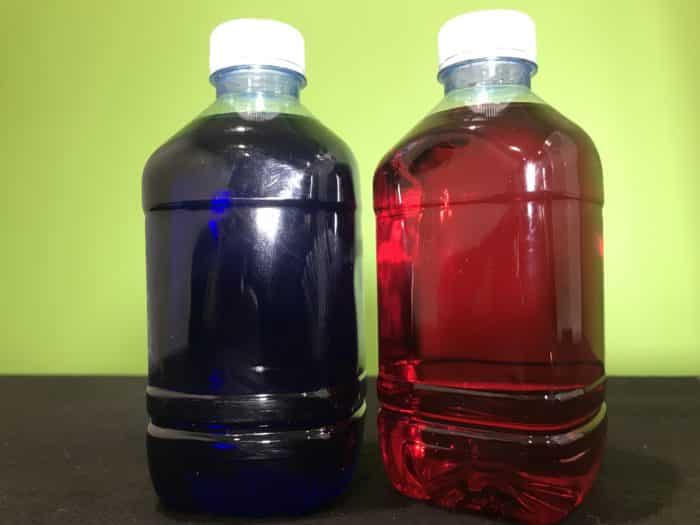
- Two identical plastic bottles with plastic screw top lids
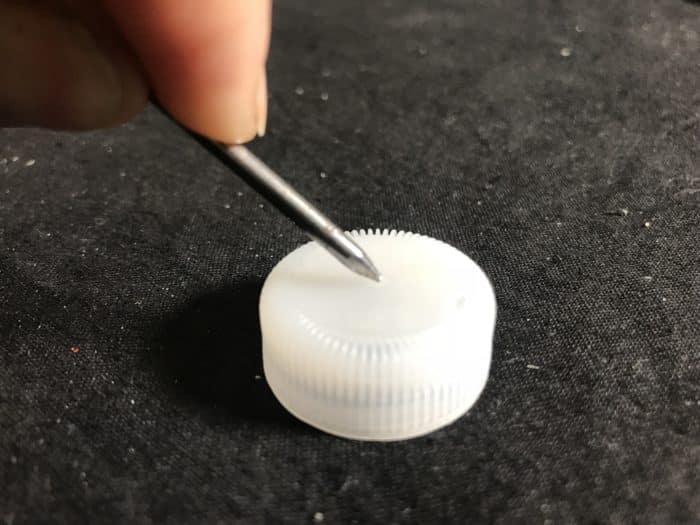
- A nail
- Adult help


SAFETY: Adults step only
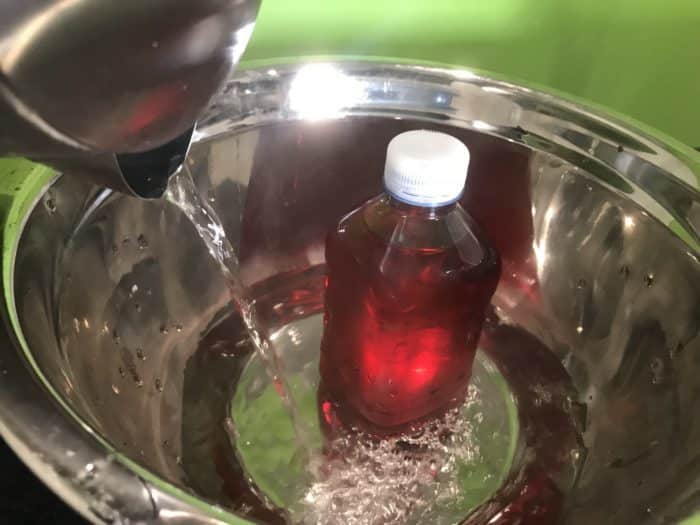
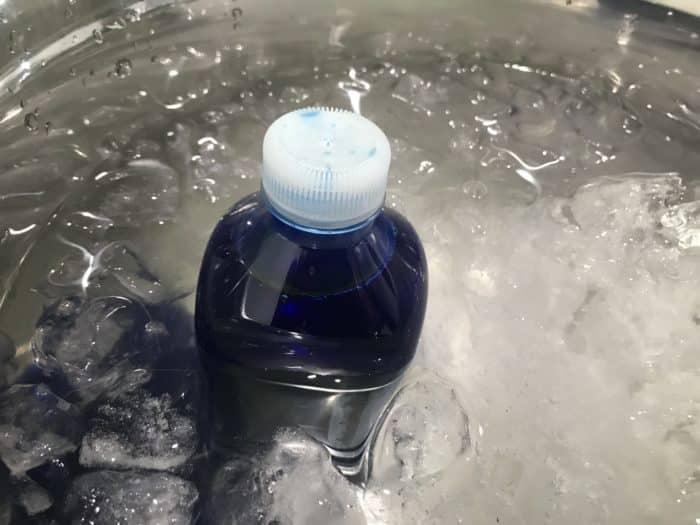
With the other plastic bottle, fill with water and add red food colouring. Screw on the lid and stand the bottle in the empty bowl. Carefully pour in the hot water around the bottle and allow this to sit until the bottle becomes warm.
Remove the warm bottle from the bowl using gloves. Once cool enough to touch the bottle with bare hands, prepare for the next step!
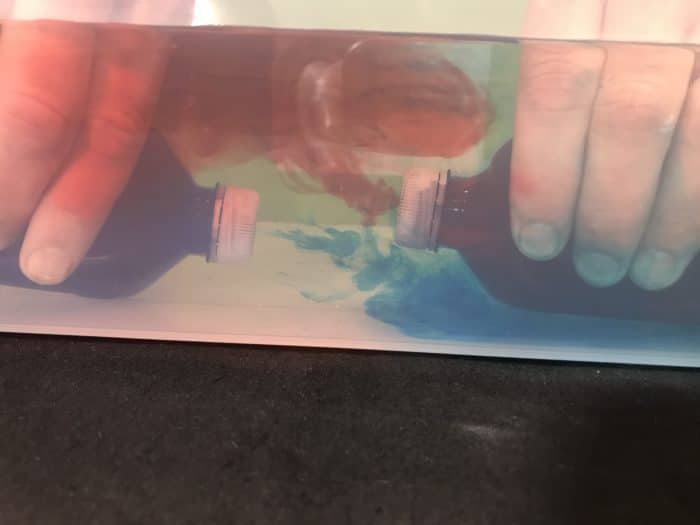
Gently lower both jars to the bottom of the large container. Make sure that each jar has the holes in the same vertical height.
Allow the coloured water to seep into the surrounding water. you can Speed the process by gently squeezing the sides of the jars, however be careful not to disturb the main body of water.

Get the Ocean Science Unit of Work!
Dive into ocean science as we look at the abiotic factors that affect life in our oceans.
- How far does light pass through water?
- How does pressure change as we go deeper underwater?
- How do ocean currents form and more!
Includes cross-curricular teaching ideas, student quizzes, a sample marking rubric, scope & sequences & more

School science visits since 2004!
– Curriculum-linked & award-winning incursions.
– Over 40 primary & high school programs to choose from.
– Designed by experienced educators.
– Over 2 million students reached.
– Face to face incursions & online programs available.
– Early learning centre visits too!
Why Does This Happen:
Warm water will float above cold layers of water because it is less dense.
In still bodies of water such as lakes and dams, very distinct layers of warm and cold water form. This phenomenon is called thermal stratification and has a profound influence on the variety of life found within the lakes and reservoirs. The warmer layer, the epilimnion, typically circulates within itself due to solar driven convection. The colder layer, the hypolimnion, tends to remain much more still, with the size of the temperature layers changing over the changing seasons.
This is why it’s often more comfortable to swim along the surface of a lake rather than dive down to the colder depths. Find out more about a thermocline, also known as a metalimnion. This is the area whereby the rapid change in water temperature occurs.
Whilst in polar regions there are complex movements of currents disturbing the thermal stratification, warmer water will still float above colder water and produce sharp changes in temperature as the depth changes. Coldwater has more dissolved oxygen and is thereby more conducive to life.
Variables to test
- What happens if you use a different liquid such as canola oil?
- Try changing the size of the bottle openings
From colour changes to slimy science, we’ve got your kitchen chemistry covered!
Get in touch with FizzicsEd to find out how we can work with your class.
Chemistry Show
Years 3 to 6
Maximum 60 students
Science Show (NSW & VIC)
60 minutes
Online Class Available
STEM Full Day Accelerator - Primary
Designed from real classroom experiences, this modular day helps you create consistently effective science learning that directly address the new curriculum with easily accessible and cost-effective materials.




























Comments